로그노멀(Log-Normal)분포 난수 생성 방법
random.lognormvariate(mu, sigma) 함수 사용
로그노멀 분포에 자연로그를 취하면 평균 mu에 표준편차 sigma를 갖는 정규분포가 됨
위키피디아 로그노멀분포:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Log-normal_distribution
Log-normal distribution - Wikipedia
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Probability distribution Log-normal Probability density functionIdentical parameter μ {\displaystyle \ \mu \ } but differing parameters σ {\displaystyle \sigma } Cumulative distribution function μ = 0 {\
en.wikipedia.org
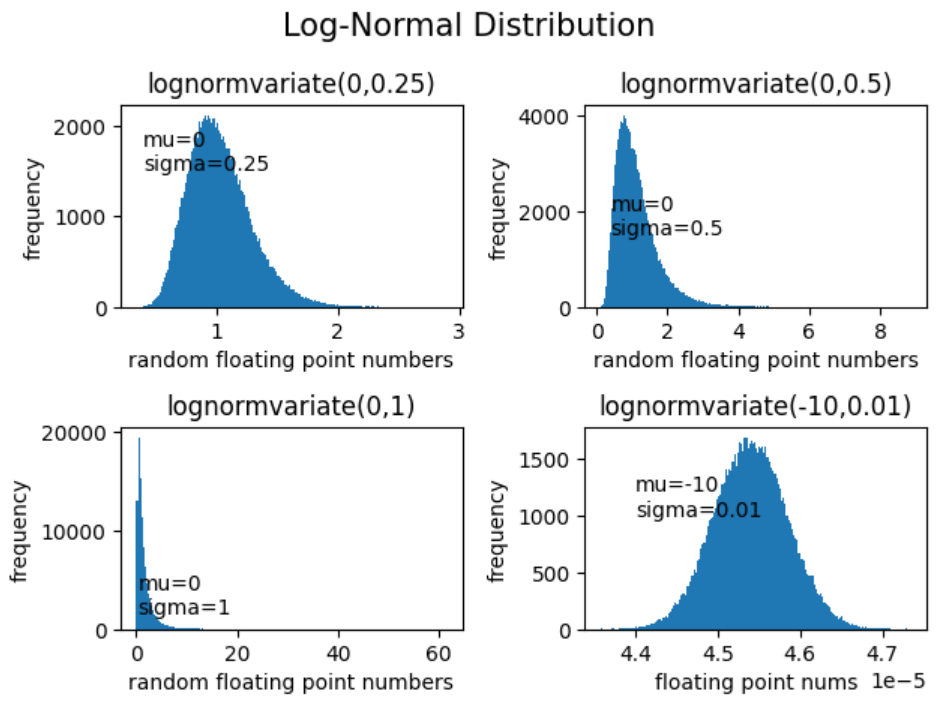
로그노멀분포 생성 및 시각화:
import random as r
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 로그-노멀분포(Log-Normal Distribution) 난수 생성
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2)
# 1. mu = 0, sigma = 0.25 인 경우
m = 0
s = 0.25
rand = [r.lognormvariate(mu=m, sigma=s) for i in range(100000)]
plt.subplot(221)
plt.hist(rand, bins=200)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xlabel("random floating point numbers")
ax.set_ylabel("frequency")
plt.title("lognormvariate("+str(m)+","+str(s)+")")
ax.text(x=0.4, y=1500, s="mu="+str(m)+"\n"+"sigma="+str(s))
# 1. mu = 0, sigma = 0.25 인 경우
m = 0
s = 0.5
rand = [r.lognormvariate(mu=m, sigma=s) for i in range(100000)]
plt.subplot(222)
plt.hist(rand, bins=200)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xlabel("random floating point numbers")
ax.set_ylabel("frequency")
plt.title("lognormvariate("+str(m)+","+str(s)+")")
ax.text(x=0.4, y=1500, s="mu="+str(m)+"\n"+"sigma="+str(s))
# 1. mu = 0, sigma = 0.25 인 경우
m = 0
s = 1
rand = [r.lognormvariate(mu=m, sigma=s) for i in range(100000)]
plt.subplot(223)
plt.hist(rand, bins=200)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xlabel("random floating point numbers")
ax.set_ylabel("frequency")
plt.title("lognormvariate("+str(m)+","+str(s)+")")
ax.text(x=0.4, y=1500, s="mu="+str(m)+"\n"+"sigma="+str(s))
# 1. mu = 0, sigma = 0.25 인 경우
m = -10
s = 0.01
rand = [r.lognormvariate(mu=m, sigma=s) for i in range(100000)]
plt.subplot(224)
plt.hist(rand, bins=200)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xlabel("floating point nums")
ax.set_ylabel("frequency")
plt.title("lognormvariate("+str(m)+","+str(s)+")")
ax.text(x=0.000044, y=1000, s="mu="+str(m)+"\n"+"sigma="+str(s))
fig.suptitle("Log-Normal Distribution", fontsize=15)
plt.tight_layout()
파레토(Pareto)분포 난수 생성 방법
random. paretovariate (alpha) 함수 사용
위키피디아 파레토분포:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pareto_distribution
Pareto distribution - Wikipedia
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Probability distribution Pareto Type I Probability density functionPareto Type I probability density functions for various α {\displaystyle \alpha } with x m = 1. {\displaystyle x_{\mathrm {m} }=1.} As α → ∞ , {\
en.wikipedia.org
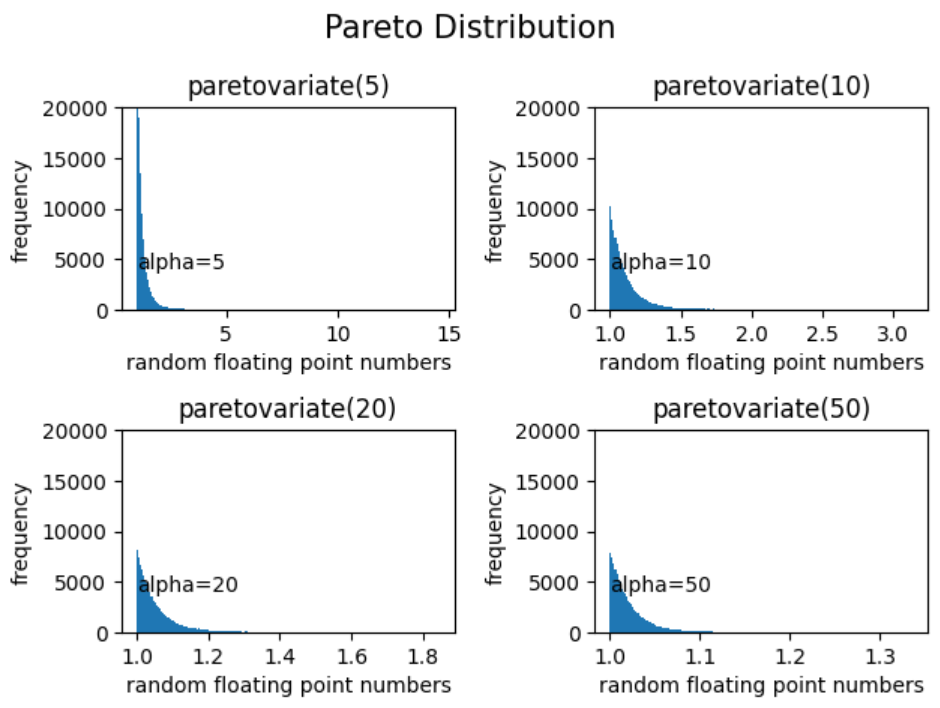
파레토 분포 난수 생성 및 시각화:
import random as r
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 파레토 분포(Pareto Distribution) 난수 생성
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2)
ylim = 20000
# 1. alpha = 5 인 경우
a = 5
rand = [r.paretovariate(alpha=a) for i in range(100000)]
plt.subplot(221)
plt.hist(rand, bins=200)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xlabel("random floating point numbers")
ax.set_ylabel("frequency")
ax.set_ylim(0,ylim)
plt.title("paretovariate("+str(a)+")")
ax.text(x=1, y=4000, s="alpha="+str(a))
# 2. alpha = 10 인 경우
a = 10
rand = [r.paretovariate(alpha=a) for i in range(100000)]
plt.subplot(222)
plt.hist(rand, bins=200)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xlabel("random floating point numbers")
ax.set_ylabel("frequency")
ax.set_ylim(0,ylim)
plt.title("paretovariate("+str(a)+")")
ax.text(x=1, y=4000, s="alpha="+str(a))
# 3. alpha = 20 인 경우
a = 20
rand = [r.paretovariate(alpha=a) for i in range(100000)]
plt.subplot(223)
plt.hist(rand, bins=200)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xlabel("random floating point numbers")
ax.set_ylabel("frequency")
ax.set_ylim(0,ylim)
plt.title("paretovariate("+str(a)+")")
ax.text(x=1, y=4000, s="alpha="+str(a))
# 4. alpha = 50 인 경우
a = 50
rand = [r.paretovariate(alpha=a) for i in range(100000)]
plt.subplot(224)
plt.hist(rand, bins=200)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xlabel("random floating point numbers")
ax.set_ylabel("frequency")
ax.set_ylim(0,ylim)
plt.title("paretovariate("+str(a)+")")
ax.text(x=1, y=4000, s="alpha="+str(a))
fig.suptitle("Pareto Distribution", fontsize=15)
plt.tight_layout()
웨이블(Weibull)분포 난수 생성 방법
random. weibullvariate(alpha, beta) 함수 사용
고장모드, 신뢰성 분석에 많이 사용함
위키피디아 웨이블분포:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Weibull_distribution
Weibull distribution - Wikipedia
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Continuous probability distribution Weibull (2-parameter) Probability density function Cumulative distribution functionParameters λ ∈ ( 0 , + ∞ ) {\displaystyle \lambda \in (0,+\infty )\,} scale k ∈ ( 0 , + ∞
en.wikipedia.org
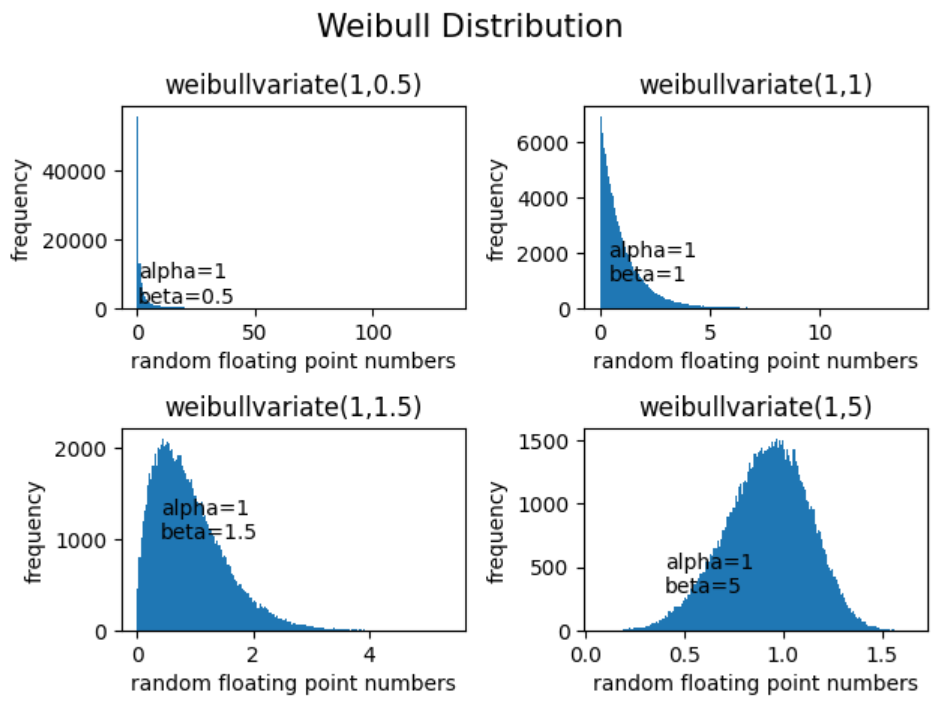
웨이블 분포 난수 생성 및 시각화:
import random as r
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 웨이블 분포 (Weibull Distribution) 난수 생성
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2)
# 1. alpha = beta = 0.5 인 경우
a = 1
b = 0.5
rand = [r.weibullvariate(alpha=a,beta=b) for i in range(100000)]
plt.subplot(221)
plt.hist(rand, bins=200)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xlabel("random floating point numbers")
ax.set_ylabel("frequency")
plt.title("weibullvariate("+str(a)+","+str(b)+")")
ax.text(x=0.4, y=1500, s="alpha="+str(a)+"\n"+"beta="+str(b))
# 2. alpha =5, beta =1
a = 1
b = 1
rand = [r.weibullvariate(alpha=a,beta=b) for i in range(100000)]
plt.subplot(222)
plt.hist(rand, bins=200)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xlabel("random floating point numbers")
ax.set_ylabel("frequency")
plt.title("weibullvariate("+str(a)+","+str(b)+")")
ax.text(x=0.4, y=1000, s="alpha="+str(a)+"\n"+"beta="+str(b))
# 3. alpha =1, beta =3
a = 1
b = 1.5
rand = [r.weibullvariate(alpha=a,beta=b) for i in range(100000)]
plt.subplot(223)
plt.hist(rand, bins=200)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xlabel("random floating point numbers")
ax.set_ylabel("frequency")
plt.title("weibullvariate("+str(a)+","+str(b)+")")
ax.text(x=0.4, y=1000, s="alpha="+str(a)+"\n"+"beta="+str(b))
# 4. alpha =2, beta =2
a = 1
b = 5
rand = [r.weibullvariate(alpha=a,beta=b) for i in range(100000)]
plt.subplot(224)
plt.hist(rand, bins=200)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xlabel("random floating point numbers")
ax.set_ylabel("frequency")
plt.title("weibullvariate("+str(a)+","+str(b)+")")
ax.text(x=0.4, y=300, s="alpha="+str(a)+"\n"+"beta="+str(b))
fig.suptitle("Weibull Distribution", fontsize=15)
plt.tight_layout()'파이썬 > 난수 생성' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 파이썬 랜덤(Random) 뽑기 총정리 - 균등분포, 정규분포 등 다양한 통계 분포로 뽑는법 (2) | 2023.12.31 |
|---|---|
| 파이썬 랜덤(Random) 뽑기 - 지수분포, 감마분포 (3) | 2023.12.30 |
| 파이썬 랜덤(Random) 뽑기 - 정규분포, 베타분포, 삼각분포 (2) | 2023.12.29 |
| 파이썬 랜덤(Random) 뽑기 - 균등분포 (0) | 2023.12.29 |


